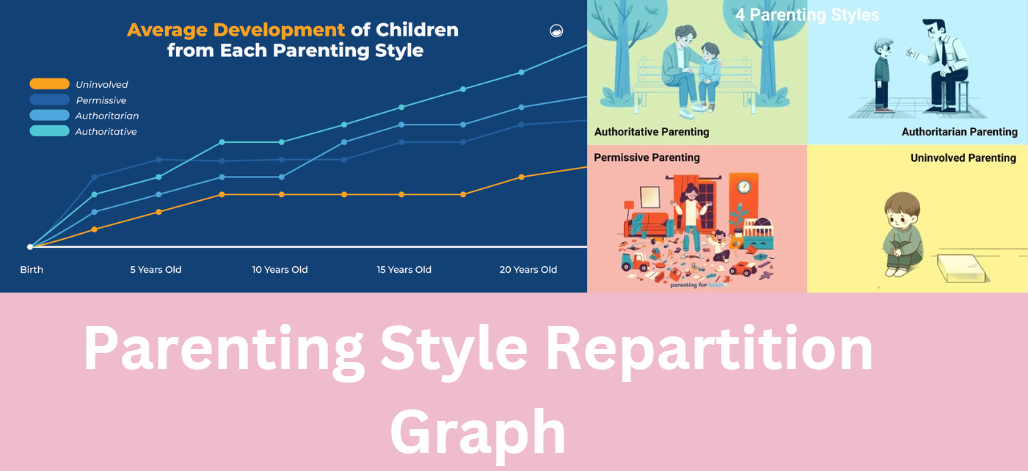
The parenting style repartition graph is a powerful tool used to analyze and visualize how parents approach raising their children. Understanding the parenting style repartition graph not only helps professionals but also offers valuable insights for parents themselves.
Parents can reflect on what they are doing and compare this to broader trends in order to make the necessary amendments to their ways of parenting to better suit their children’s needs.
This paper discusses the aspects of the parenting style repartition graph, its importance, and how this may be used to come up with better parenting principles globally.
What Is a Parenting Style Repartition Graph?
A parenting style repartition graph is an illustration that shows the percentage or percentage proportion of parents who follow each of the four identified parenting styles.
In general, these graphs tend to be pie charts, bar graphs, or any other statistical representation that best brings out the data. This information usually comes from surveys, interviews, and even observational studies wherein parents do share their behavior and attitude.
A parenting style repartition graph might reveal that 50 percent of the parents in a given region are authoritative, 25 percent authoritarian, 15 percent permissive, and 10 percent uninvolved. The data thus opens up avenues to discover which parenting styles are most prevalent, what cultural, economic, or social factors determine the prevalence of these trends, and so on.
Such graphs are of significant value to researchers in this field, particularly for comparing the results cross-demographically, regionally, or culturally.
The Four Parenting Styles: Insights from the Graph
The parenting style repartition graph breaks down parenting methods into the following categories, each with distinct characteristics and implications:

Authoritative Parenting combines high responsiveness with high demandingness. Parents in this category establish clear boundaries while fostering open communication and emotional support.
Children raised by authoritative parents often exhibit high self-esteem, strong social skills, and academic success. In most parenting style repartition graphs, authoritative parenting occupies the largest segment, especially in societies that emphasize balanced child development.
Authoritarian Parenting emphasizes strict rules and high expectations but offers limited emotional responsiveness. These parents value discipline and control, often enforcing rules rigidly.
While this approach can instill obedience, it may hinder emotional expression and independence. In parenting style repartition graphs, authoritarian parenting is often prominent in cultures prioritizing hierarchy and structure.
Permissive Parenting prioritizes emotional warmth over discipline. These parents avoid confrontation and allow their children significant freedom. While permissive parenting fosters close emotional bonds, it can lead to challenges like poor self-discipline and boundary-setting in children.
The parenting style repartition graph often shows permissive parenting as a smaller segment, reflecting societies where structure is valued.
Uninvolved Parenting reflects minimal responsiveness and low expectations. Parents in this category are disengaged, often due to stress, lack of resources, or limited knowledge about effective parenting.
This style is associated with negative outcomes for children, including poor academic performance and social skills. In most graphs, uninvolved parenting represents the smallest percentage, indicating its rarity but underscoring its importance for intervention efforts.
Applications of Parenting Style Repartition Graphs
The parenting style repartition graph offers actionable insights for various stakeholders:
Research and Analysis:
Researchers use these graphs to identify patterns in parenting across cultures or regions. For instance, a study might compare the prevalence of authoritarian parenting in collectivist societies versus individualist ones.
Parenting Workshops:
Educators and coaches use data from the graph to design workshops that address specific trends. If permissive parenting is dominant in a region, workshops may focus on setting boundaries and enforcing discipline.
Parent Reflection and Growth:
Parents can use the graph to evaluate their own approach. By understanding where they fall on the spectrum, they can adopt more effective strategies that align with their goals for their children.
FAQs About Parenting Style Repartition Graphs
1. Why is the parenting style repartition graph important?
The graph provides a clear overview of how parenting styles are distributed within a population, helping professionals and parents identify trends, cultural influences, and potential areas for improvement.
2. What factors influence the data in a parenting style repartition graph?
Cultural norms, socioeconomic status, education levels, and personal beliefs all play significant roles in shaping parenting styles.
3. How can parents benefit from understanding these graphs?
Parents can reflect on their methods, compare them to broader trends, and make adjustments to adopt a more balanced and effective parenting approach.
4. What parenting style is most effective?
Research consistently supports authoritative parenting as the most effective style for fostering healthy development, balancing discipline with emotional warmth.
5. Are parenting styles fixed, or can they change?
Parenting styles are not static; they can evolve over time based on life experiences, education, and access to resources.
Visualizing Parenting Trends
To fully understand the parenting style repartition graph, it is helpful to visualize the data. For instance, a pie chart might depict how parenting styles are distributed across different regions, while a bar graph could show variations based on socioeconomic factors. Such visual aids make complex data more accessible and engaging.
Adding in with country-to-country comparisons or changes over time makes such a graph even worthwhile. It can help parents and educators pinpoint challenges and successes within the demographics represented.
Conclusion
This parenting style repartition graph is absolutely an essential tool in understanding why parenting approaches vary from one population to another, categorizing parents into authoritative, authoritarian, permissive, and uninvolved styles-it lays bare the dynamics shaping child development. In research, education, or parental use, it provides highly valuable insight that drives change for better.
Affiliated Posts Like Parenting Style Repartition Graph
The Ultimate Guide to Mollar CGT 20750 Drawing: Unleashing Precision and Excellence
6608101372 Filtro de Aire: Everything You Need to Know About This Essential Air Filter
Does Butomart Use Albatross America Inc.? Let’s Dive into What a Partnership Could Mean for You






